
Essential PPE in the Food Industry: What You Need to Know
Overwhelmed by PPE options for food safety? Master your PPE selection for food workers safety with these practical tips.

Get 10€ off on your first order!
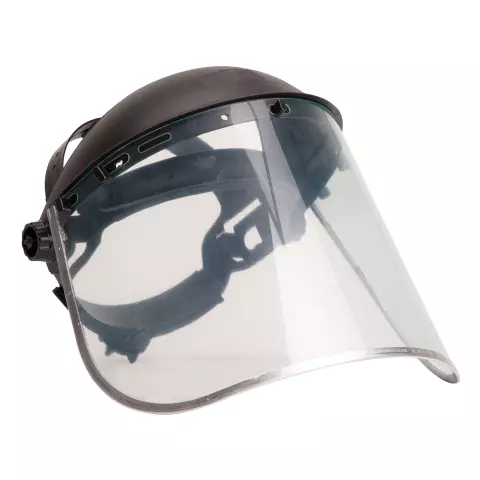
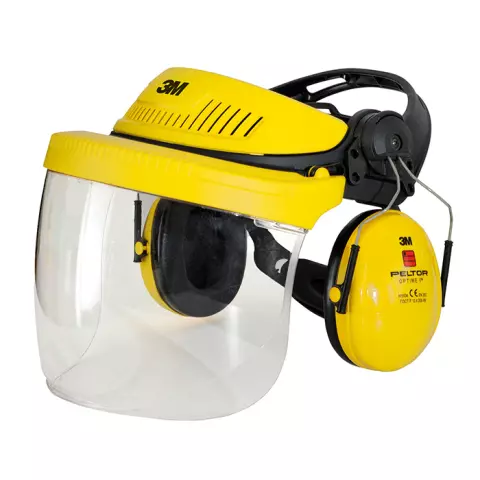
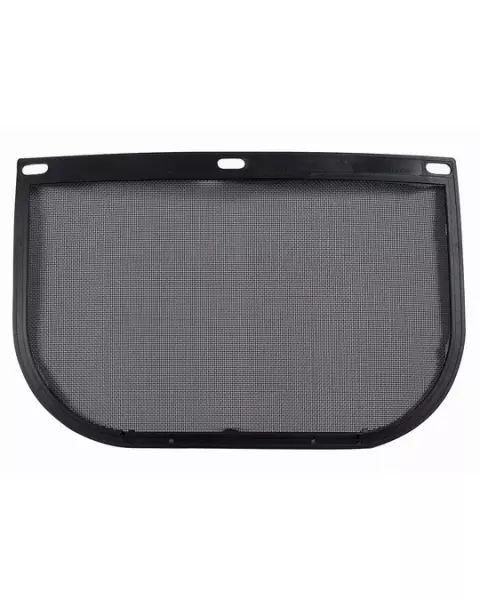
When working with chemical hazards, ensures comprehensive protection against splashes, vapours, and particulate matter to support safe and efficient work. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the critical factors to consider when selecting a chemical protection face shield, ensuring both safety and practicality. Whether you’re handling volatile chemicals in a laboratory or industrial setting, you’ll find all the information you need here. For a broader overview of face shields, explore our main article: How to Choose the Right Face Shields – A Buyer’s Guide.
When choosing a chemical protection face shield, keep the following in mind:
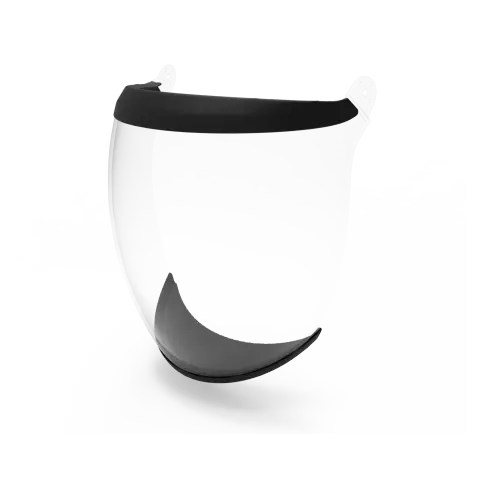
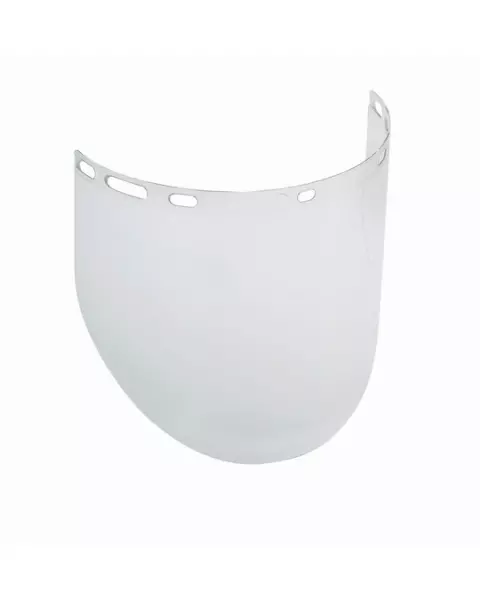
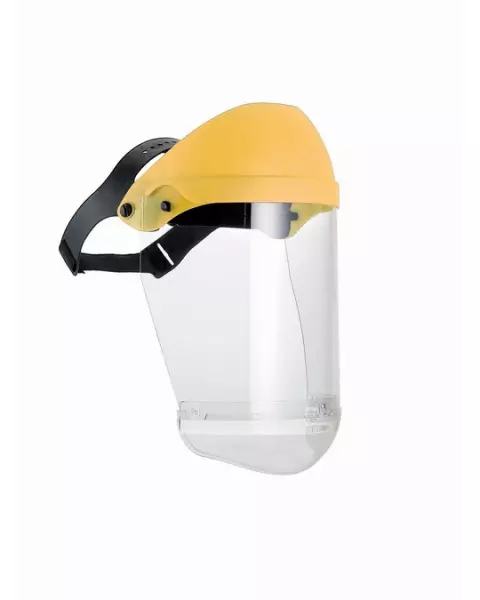
Face shields designed for chemical protection are typically made from materials like polycarbonate or acetate, which resist corrosion and ensure clear visibility. Acetate offers superior resistance to solvents and harsh chemicals, making it ideal for lab and industrial use.

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/package

/piece

/package

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/piece

/package

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/piece

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/package
/package

/package
Ensure the face shield meets EN 166 safety standards for personal protective equipment (PPE), which cover impact resistance, optical clarity, and chemical splash protection. This guarantees impact resistance and chemical splash protection. Learn more about EN Standards from this guide by Wise Worksafe.
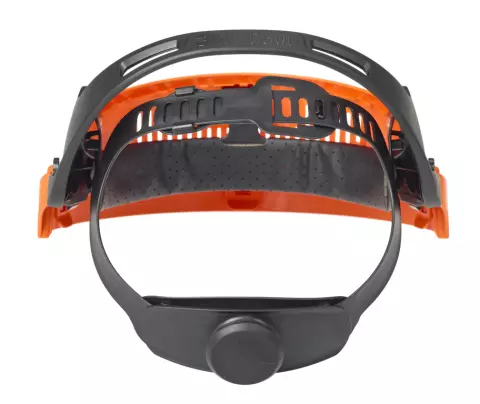
A well-fitted shield is crucial for long hours of work. Look for:
Ensure the shield integrates seamlessly with other equipment like safety glasses or respirators. Explore safety glasses for added eye protection in demanding work settings.
| Material | Strengths | Limitations |
| Polycarbonate | High impact resistance, lightweight | Limited chemical resistance |
| Acetate | Excellent chemical resistance | Less durable against impacts |
| PETG | Affordable, good visibility | May degrade with strong solvents |
Choose the material based on the specific chemicals you work with and the nature of your tasks, such as using acetate shields for protection against organic solvents or polycarbonate for general-purpose impact resistance.
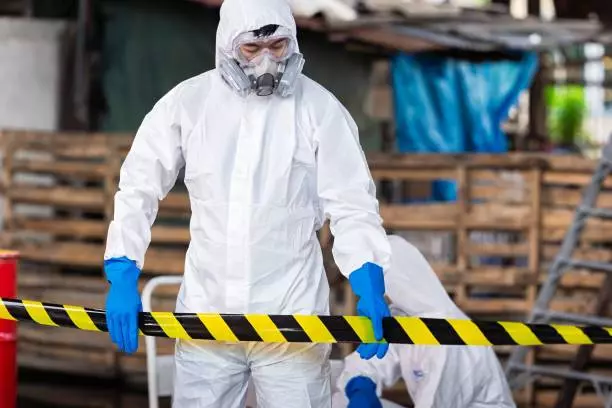

These shields provide essential protection in industries dealing with chemical splashes or vapours. Common applications include:
Each task benefits from PPE designed to address its unique challenges effectively. For more guidance on related protection, see How to Choose Safety Glasses – A Buyer’s Guide.
To ensure longevity and optimal performance, follow these care tips:
A chemical protection face shield should be replaced immediately if it shows any signs of damage or wear. Proper care and maintenance ensure durability even with regular chemical exposure. If you need a new shield, explore our selection of face shields.
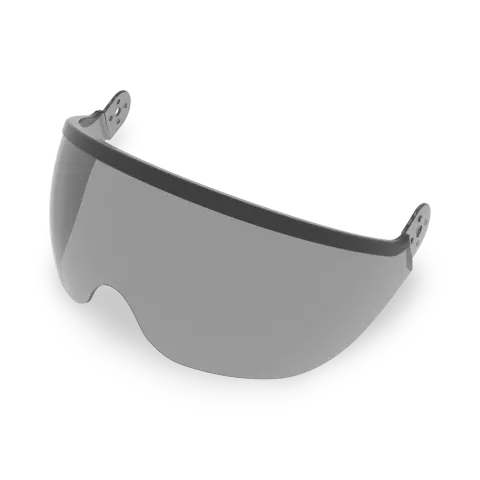
Understanding the right PPE for sight is essential in high-risk settings to ensure comprehensive protection against unique challenges like splashes, debris, or chemical vapours. In addition to chemical protection face shields, consider other PPE options:
For detailed insights, visit our guide: How to Choose the Right Welding Glasses – A Buyer’s Guide.

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/piece

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package

/package
We hope this guide has provided valuable insights into selecting the right chemical protection face shield, from material choices to key safety standards. Whether you’re working in a laboratory or dealing with industrial chemicals, we’re here to support you in making the best decision for your protection.
For a complete range of options, visit our face shields category and explore other related guides for additional safety insights.
Confidently equip yourself with the right tools to stay protected and productive. For further reading, don’t miss our main article: How to Choose the Right Face Shields – A Buyer’s Guide.
Have questions or need assistance finding the perfect face shield? Don’t hesitate to reach out—we’re always here to help ensure your safety and confidence with every choice you make.
– The Droppe Team
Yes, many face shields are designed to be worn with prescription glasses. Look for models with enough space or adjustable headbands for comfort.
Clean with mild soap and water, or use the manufacturer’s recommended cleaner. Avoid abrasive materials to prevent scratches.
Yes, most face shields are reusable if properly maintained. Replace them if they show signs of damage or wear.
No, face shields are designed for chemical splash protection, not heat. For high-temperature environments, consider using a welding helmet or heat-resistant face shield.
While a face shield protects against splashes, it does not offer protection against vapors. If working with airborne chemicals, always use a respirator.
Thank you! You've signed up for our newsletter.



















Overwhelmed by PPE options for food safety? Master your PPE selection for food workers safety with these practical tips.

Struggling to maintain clear vision in demanding environments? This guide is here to help. By the end, you’ll know exactly...

Electricians across Europe face unique challenges that require reliable safety glasses to ensure both protection and efficiency. Whether safeguarding against...

Overwhelmed by PPE options for food safety? Master your PPE selection for food workers safety with these practical tips.

Struggling to maintain clear vision in demanding environments? This guide is here to help. By the end, you’ll know exactly...

Electricians across Europe face unique challenges that require reliable safety glasses to ensure both protection and efficiency. Whether safeguarding against...
Get 10€ off on your first order!
Save 30% by buying directly from brands, and get an extra 10€ off orders over €100
Save 30% by buying directly form brands, and get an extra 10€ off orders over €100