
Essential PPE in the Food Industry: What You Need to Know
Overwhelmed by PPE options for food safety? Master your PPE selection for food workers safety with these practical tips.

Get 10€ off on your first order!
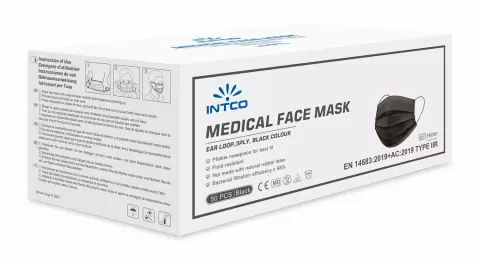
Selecting the right face mask is essential for healthcare workers to ensure protection and comfort. With so many options available, it can be difficult to choose the best one for your needs. This guide will help you make an informed decision, whether you need a surgical mask, disposable respirator, or full mask respirator.
You’ll learn about important factors like filtration efficiency, fit, comfort, and regulatory standards. We’ll provide expert advice to help you select the right mask and ensure it meets the necessary requirements for your work environment.
By the end of this guide, you’ll not only know which mask to choose, but also how to properly use and maintain it for optimal protection. We’ll also help you tackle any challenges you might face in the future, so you can stay confident in your safety at work.
For a broader understanding, see our main article on disposable respirators.
Understanding the different types of face masks available is the first step in making an informed choice. Here are the most common categories:
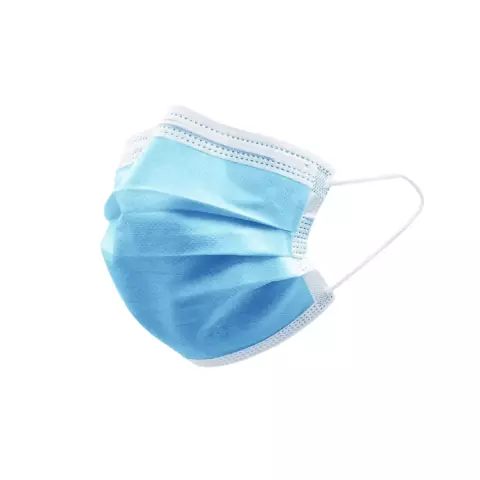
Surgical masks are fluid-resistant and protect against large droplets, splashes, or sprays of bodily or other potentially infectious fluids. However, they are not designed to filter airborne particles and may not provide a tight fit.

/package

/package

/package
/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/piece

/piece

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package
/package

/package

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package
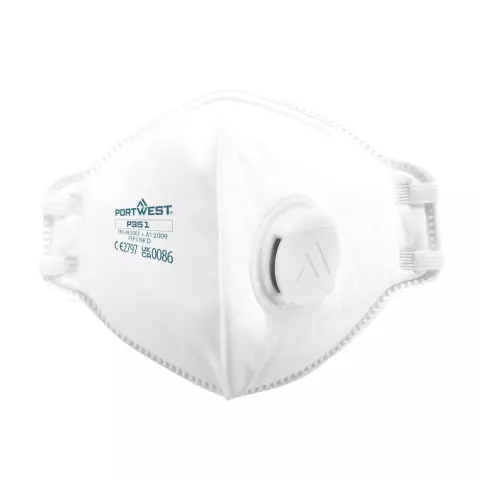
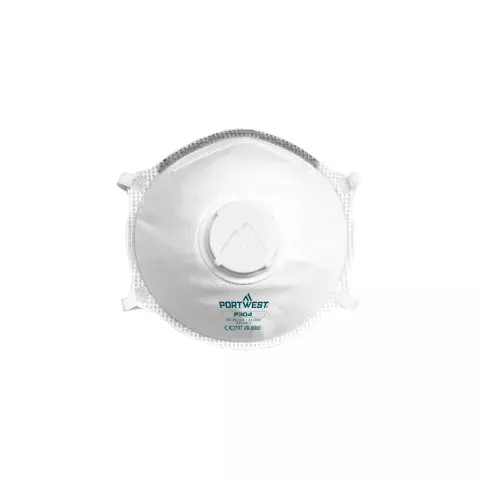
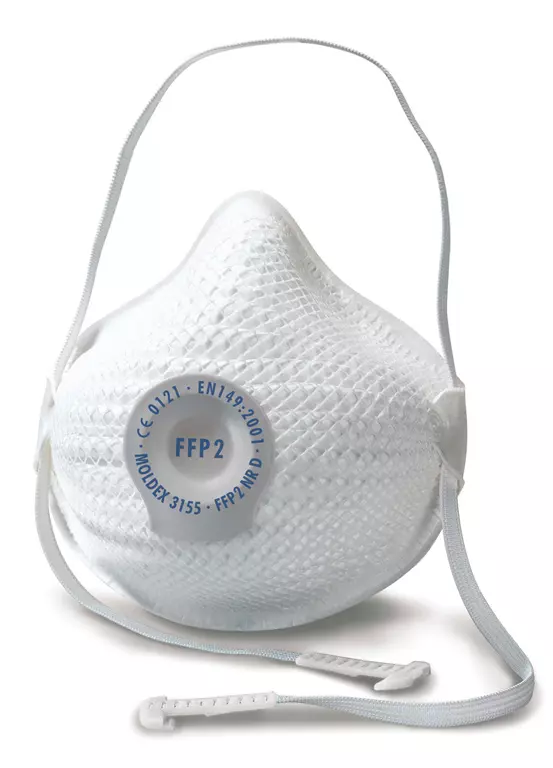
Disposable respirators, such as FFP2 and FFP3 masks, offer higher filtration efficiency and fit more snugly around the face. They are ideal for environments where exposure to airborne particles is increased. Learn more about their benefits in our guide to disposable respirators.

While less common in healthcare, full mask respirators and half mask respirators offer advanced protection in areas where contamination risks are higher. Explore their unique features in our related guides on full mask respirators and half mask respirators.
Masks should meet European standards such as EN 149, which classifies respirators based on their filtering efficiency and leakage. This standard defines three levels: FFP1, FFP2, and FFP3, with FFP3 providing the most effective filtration against airborne particles.
Healthcare professionals working in FFP2 or FFP3 masks are well-suited for environments with increased exposure risks. For detailed information about EN 149 standards, visit this guide.
A snug fit minimizes air leakage and ensures proper protection. To check for a snug fit:
Comfort is also vital, especially during extended use. Consider masks with soft, hypoallergenic materials and designs that minimize pressure on the nose and face.
A snug fit minimizes air leakage and ensures proper protection. Look for masks with adjustable nose clips and secure straps. Comfort is vital, especially during extended use.
Opt for masks that balance filtration efficiency with low breathing resistance, enabling easier and more natural breathing during wear.
Ensure your mask works well with other protective gear, such as goggles or face shields, without compromising the fit.
Check for compliance with standards such as EN 14683 (surgical masks) and EN 149 (respirators) to ensure quality and reliability. Refer to the European Commission’s PPE regulations for detailed guidelines.
| Feature | FFP1 | FFP2 | FFP3 |
| Filtration Rate | ≥ 80% | ≥ 94% | ≥ 99% |
| Breathing Resistance | Low | Moderate | High |
| Protection Level | Low-risk settings | Moderate-risk settings | Settings with elevated exposure risks |
Choosing and using a face mask effectively is crucial for ensuring both personal safety and patient care in healthcare settings. By following these best practices, you can maintain optimal protection while adhering to safety protocols.
For reliable, high-quality options, explore our disposable respirators collection. If you need more robust options, consider our full mask respirators or half mask respirators.
For further reading, visit Uvex Safety’s respirator guide.

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/piece

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package
We hope this guide has been helpful in navigating the key factors for choosing the right face mask, from filtration efficiency to fit and comfort. Whether you’re working in a high-risk healthcare setting or ensuring safety in everyday tasks, we’re here to support your needs.
To explore related products, visit our disposable respirators collection. For more insights on advanced options, check out full mask respirators and half mask respirators.
Have questions or need advice on selecting the perfect mask? Don’t hesitate to reach out—we’re always here to help ensure your safety and confidence with every purchase.
– The Droppe Team
Ensure a snug fit by checking for air leaks around the edges and using a fit test. Masks with adjustable nose clips and secure straps help achieve a better fit.
No, disposable respirators are designed for single-use only. Reusing them may compromise their effectiveness.
FFP2 masks offer moderate protection with a filtration rate of 94%, while FFP3 masks provide higher protection with a filtration rate of 99%.
Surgical masks protect against large droplets but may not filter airborne particles as effectively as respirators like FFP2 or FFP3.
Yes, many masks are compatible with glasses. Look for masks with adjustable nose bridges to prevent fogging.
Thank you! You've signed up for our newsletter.



















Overwhelmed by PPE options for food safety? Master your PPE selection for food workers safety with these practical tips.

Struggling to maintain clear vision in demanding environments? This guide is here to help. By the end, you’ll know exactly...

Electricians across Europe face unique challenges that require reliable safety glasses to ensure both protection and efficiency. Whether safeguarding against...

Overwhelmed by PPE options for food safety? Master your PPE selection for food workers safety with these practical tips.

Struggling to maintain clear vision in demanding environments? This guide is here to help. By the end, you’ll know exactly...

Electricians across Europe face unique challenges that require reliable safety glasses to ensure both protection and efficiency. Whether safeguarding against...
Get 10€ off on your first order!
Save 30% by buying directly from brands, and get an extra 10€ off orders over €100
Save 30% by buying directly form brands, and get an extra 10€ off orders over €100