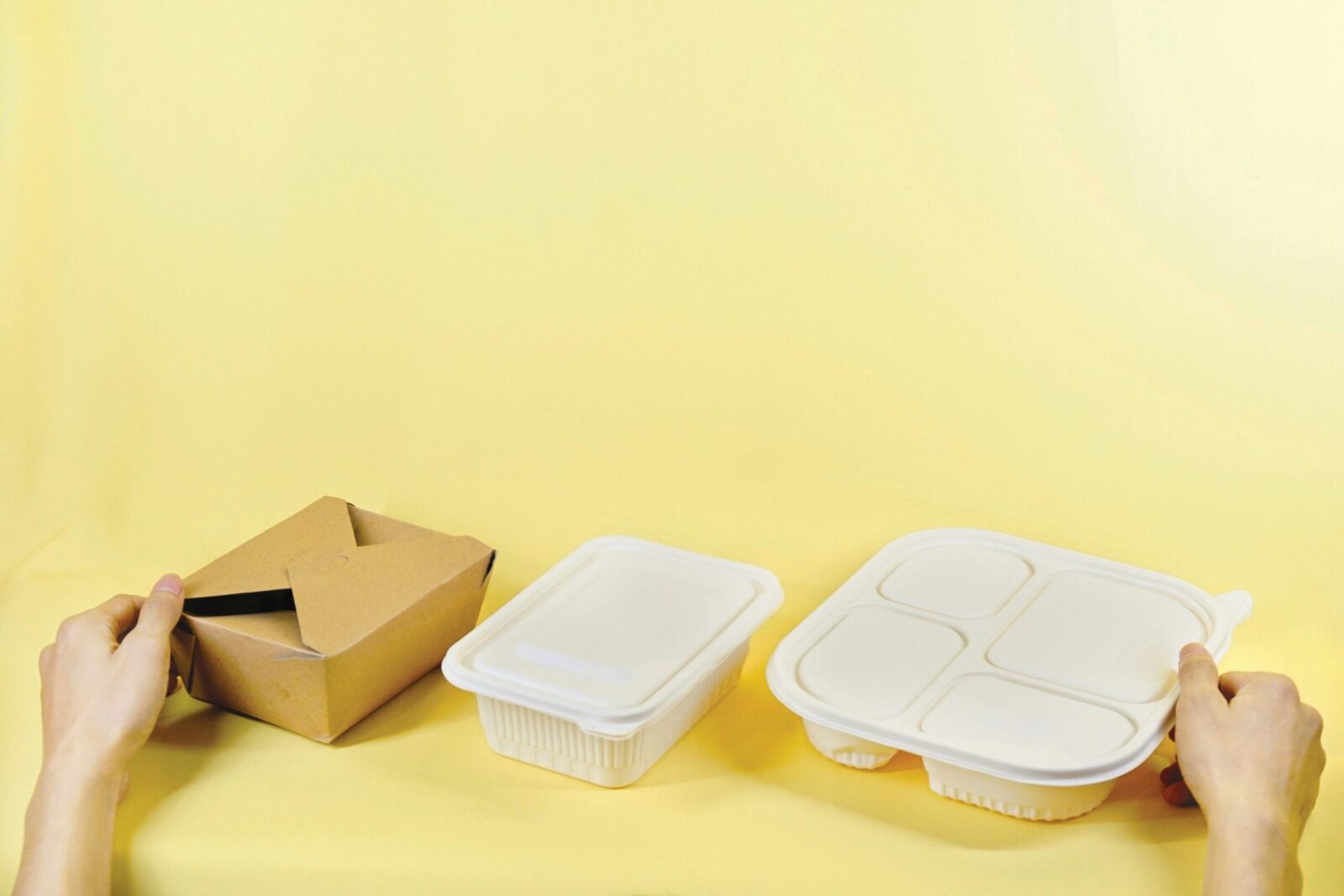

What is the EN 13432 Standard?
Biodegradable packaging has become increasingly important in recent years as the world seeks more sustainable alternatives to traditional packaging materials....

Get 10€ off on your first order!
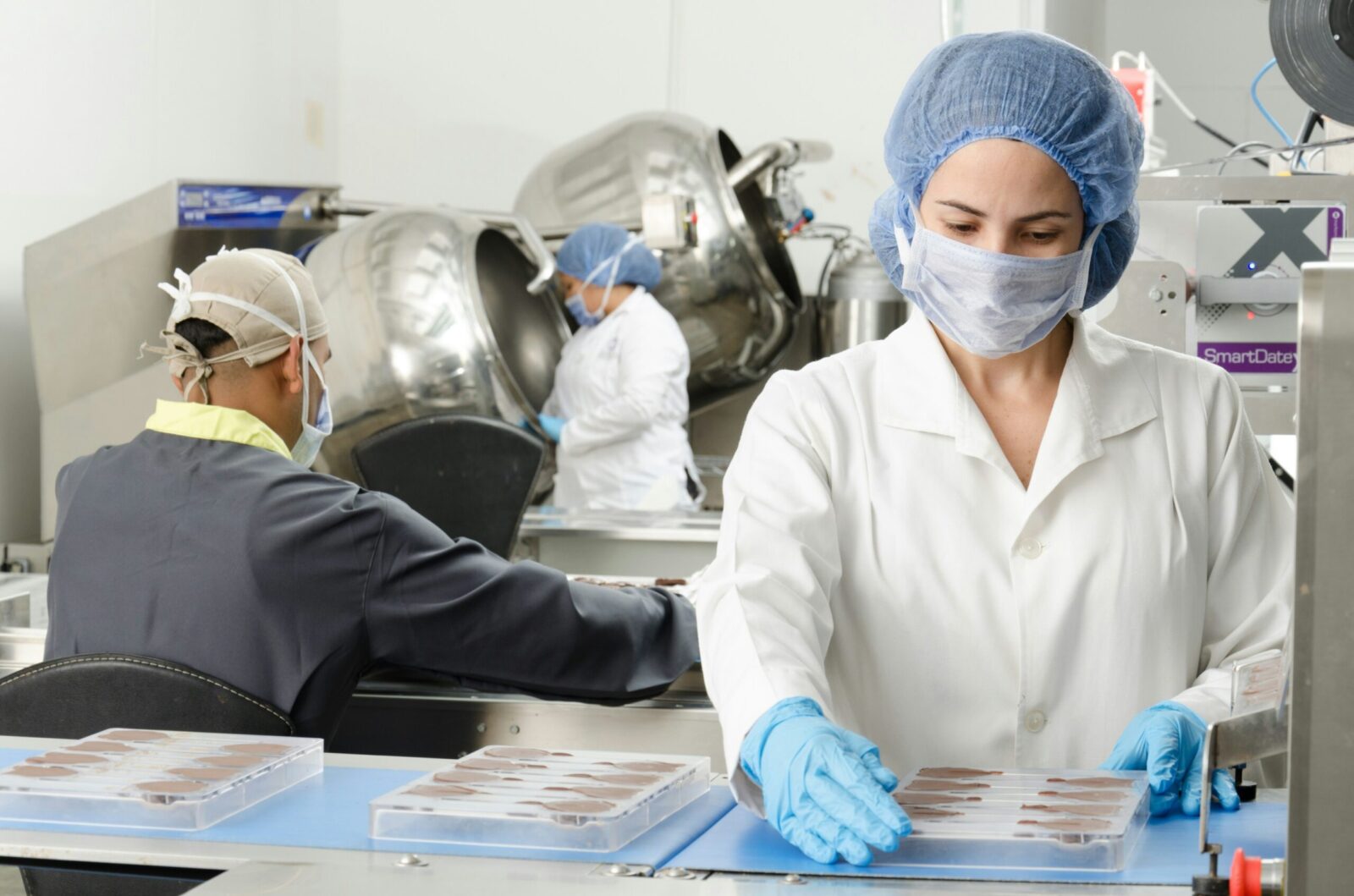
ISO 22000 is an internationally recognized standard that sets the requirements for a Food Safety Management System (FSMS). Designed to ensure food safety across the entire supply chain, this standard helps organizations identify and control food safety hazards systematically. It integrates principles from the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system and aligns with other management standards, such as ISO 9001.

ISO 22000 is structured around several essential elements that enable organizations to manage food safety effectively:
Effective communication is crucial for identifying and managing food safety hazards. ISO 22000 emphasizes the importance of transparent communication among stakeholders, including suppliers, customers, and regulatory bodies, to maintain safety across the food chain.

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/piece

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package
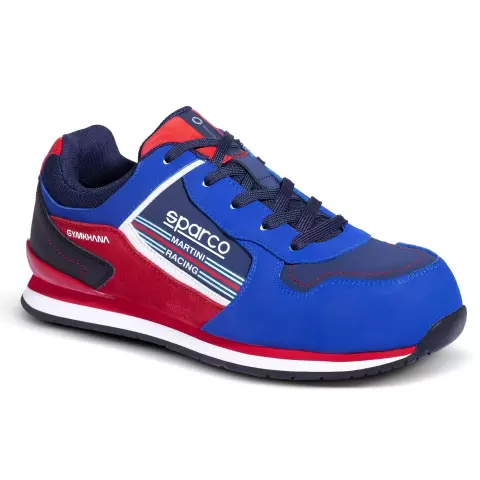

/pair

/pair
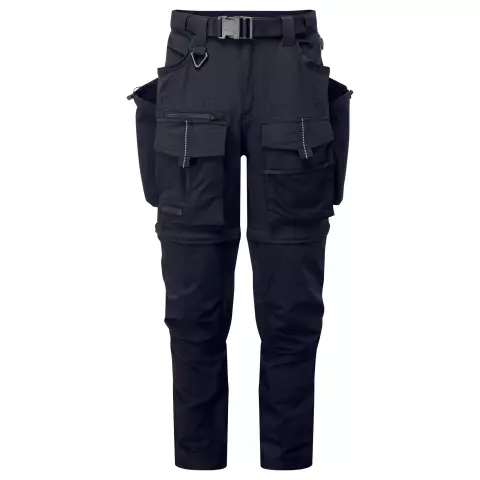

/package
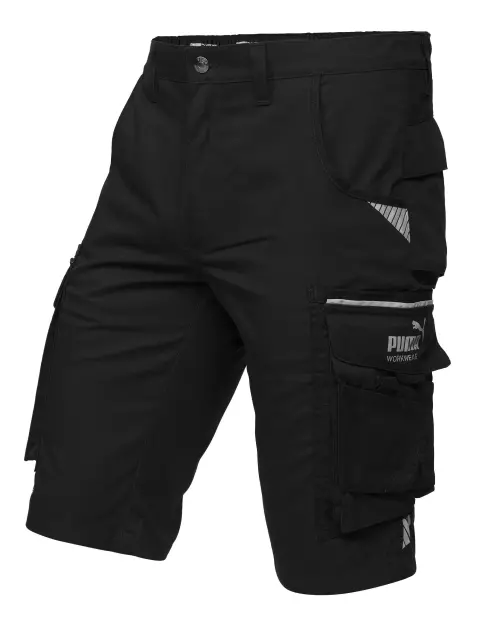

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/package
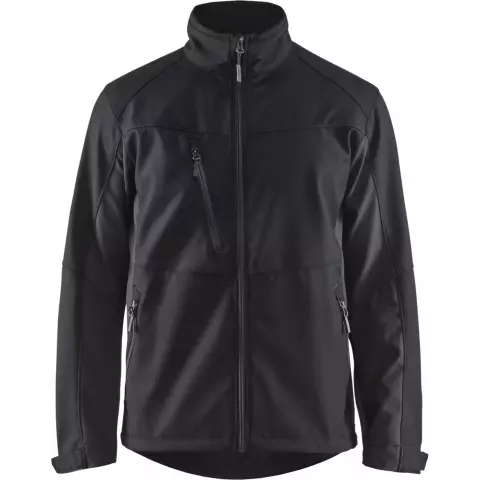

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/package
/package
The standard adopts a structured management system approach, incorporating the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle. This ensures continuous improvement in food safety performance by systematically addressing challenges and implementing solutions.
PRPs establish the basic conditions needed to maintain a hygienic environment. These include facility maintenance, sanitation, employee hygiene, and more, forming the foundation for food safety.
ISO 22000 incorporates HACCP principles to identify, evaluate, and control food safety hazards. This proactive approach ensures risks are managed before they impact the end product.
Adopting ISO 22000 can bring several advantages to organizations within the food chain:
By systematically managing food safety hazards, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses, ensuring the safety of their products.
Compliance with ISO 22000 helps organizations meet national and international food safety regulations, avoiding legal complications.
ISO 22000 certification signals reliability, opening doors to new markets and clients who require adherence to recognized food safety standards.
Demonstrating a commitment to food safety can enhance trust and loyalty among consumers, boosting brand reputation.
Achieving ISO 22000 certification involves a structured approach:
Evaluate your organization’s current food safety practices against ISO 22000 requirements to identify areas for improvement.
Establish robust policies, procedures, and controls to address and manage food safety hazards effectively.
Provide training to employees at all levels to ensure they understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining food safety.
Conduct regular internal audits to assess the FSMS’s effectiveness and identify opportunities for continuous improvement.
Engage an accredited certification body to evaluate your FSMS and verify compliance with ISO 22000 standards.
ISO 22000 is not just a certification; it’s a commitment to food safety and quality. By implementing this standard, organizations can ensure the delivery of safe, high-quality products to consumers while improving operational efficiency and business performance.
Whether you’re looking to expand your market, meet regulatory requirements, or enhance customer trust, ISO 22000 provides a robust framework for managing food safety hazards.
The certification is applicable to organizations of all sizes and types within the food industry, including food manufacturers, processors, distributors, and caterers.
The time required to achieve the certification depends on various factors, such as the organization’s size, complexity, and readiness. On average, the process may take several months to a year or more.
The certification is not mandatory by law. However, many organizations choose to pursue certification voluntarily to demonstrate their commitment to food safety and gain a competitive edge in the market.

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/piece

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package
By following the guidelines and requirements, organizations can establish effective food safety management systems, mitigate risks, and ensure the production of safe and high-quality food products. The implementation of ISO 22000 brings multiple benefits, including enhanced food safety, increased customer confidence, and improved risk management. By obtaining the certification, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to excellence and gain a competitive advantage in the global food market.
Moreover, the certification is not only beneficial for the organizations themselves but also for consumers. When a company is ISO 22000 certified, it means that they have met internationally recognized standards for food safety management. This provides consumers with the assurance that the food products they are purchasing have been produced under strict guidelines to ensure their safety and quality.
Additionally, achieving ISO 22000 certification involves a thorough evaluation of the entire food production process, from sourcing raw materials to the final product distribution. This comprehensive approach helps organizations identify potential risks and implement measures to control and prevent food safety hazards at every stage of the supply chain. By proactively addressing these risks, companies can not only protect their consumers but also safeguard their reputation and brand integrity in the market.
For more details about ISO 22000 and food safety management systems, refer to these sources:
By taking the steps to implement ISO 22000, you’re not just ensuring compliance—you’re building a safer and more trustworthy food supply chain.
Thank you! You've signed up for our newsletter.



















Biodegradable packaging has become increasingly important in recent years as the world seeks more sustainable alternatives to traditional packaging materials....

Safety is a definite concern in industries where employees are exposed to hazardous conditions. Safety footwear plays a critical role...

In today’s busy world, safety is paramount. Whether you’re working in construction, transportation, or any other industry where visibility is...

Biodegradable packaging has become increasingly important in recent years as the world seeks more sustainable alternatives to traditional packaging materials....

Safety is a definite concern in industries where employees are exposed to hazardous conditions. Safety footwear plays a critical role...

In today’s busy world, safety is paramount. Whether you’re working in construction, transportation, or any other industry where visibility is...
Get 10€ off on your first order!
Save 30% by buying directly from brands, and get an extra 10€ off orders over €100
Save 30% by buying directly form brands, and get an extra 10€ off orders over €100