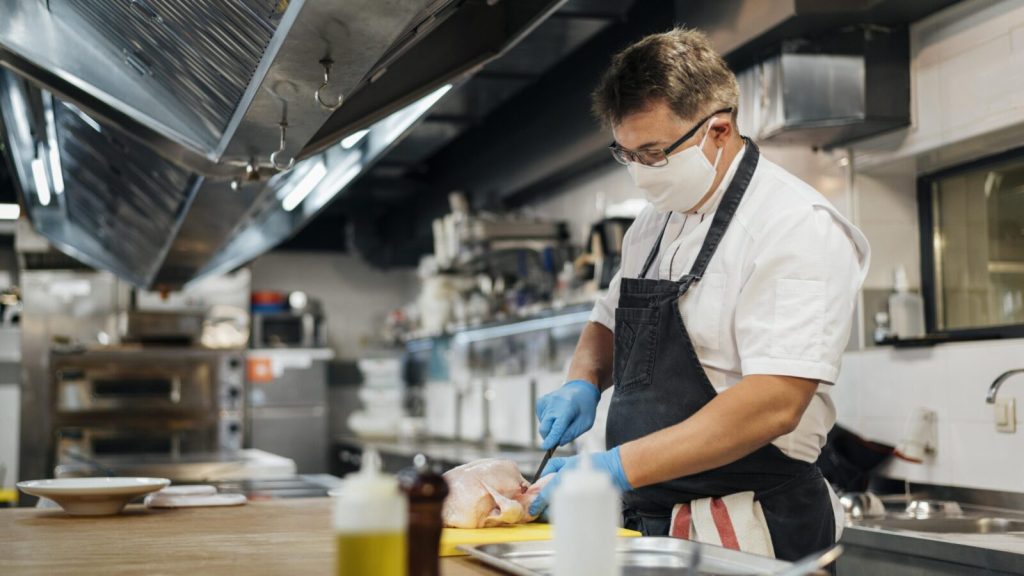

Essential PPE in the Food Industry: What You Need to Know
Overwhelmed by PPE options for food safety? Master your PPE selection for food workers safety with these practical tips.

Get 20€ off on your first order!
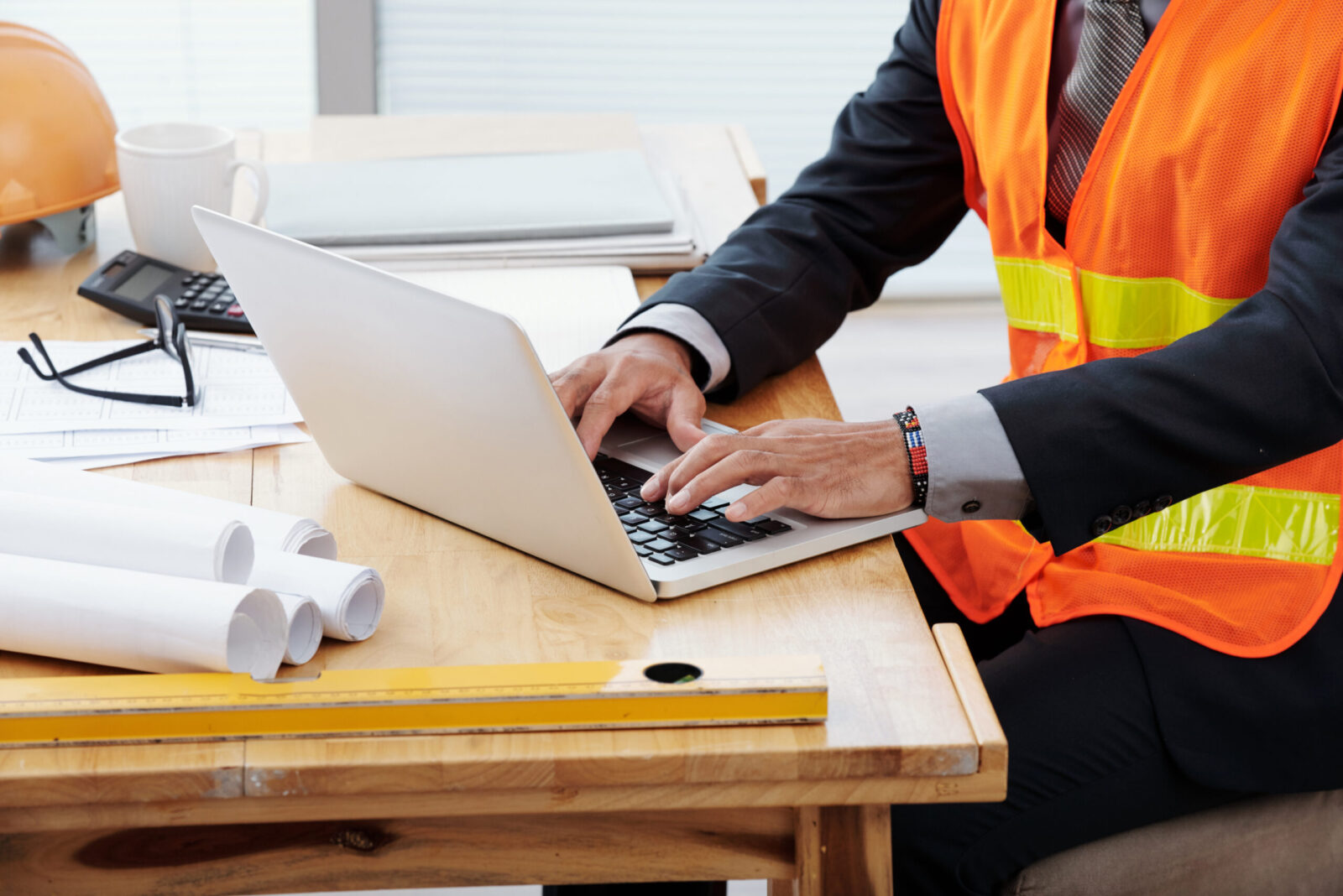
Safety audits are crucial to employee safety and business productivity. New safety dangers arise when technology, workplace procedures, and diverse workforces evolve. Safety audits help companies avoid accidents and comply with rules. This tutorial will explain safety audit, their advantages, and how to perform them in the workplace.
A comprehensive, documented safety audit evaluates an organization’s health and safety management system. It proactively identifies and mitigates dangers before they cause accidents or injuries.

/piece

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/piece

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/piece

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/package

/package

/package

/package

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/pair

/package

/pair

/pair

/package

/package
/package

/package
Safety audits detect workplace dangers, verify compliance with rules and business policy, and evaluate control methods.
Safety audits examine workplace safety culture rather than particular areas or procedures.
Safety audits differ from inspections in scope and frequency:
Audits obtain more data through interviews, record reviews, surveys, and practice observation. Safety audits’ comprehensive findings enable strategic workplace safety choices and investments.
The main safety audit goals are:
Employee safety and risk management are greatly improved by regular safety audits. Consistent safety audits provide several benefits:
This is the main advantage. Safety audits detect and resolve dangers, preventing mishaps and reducing illnesses, injuries, and deaths.
Cal/OSHA audits decreased injuries without employment losses, according to a 2012 study. The research found 9.4% fewer injury claims and 26% lower workers’ compensation expenses.
Safety audits verify compliance with safety requirements. This decreases the danger of legal sanctions, fines, and closures for noncompliance.
Accident prevention via audits reduces property damage, penalties, medical treatment, increased insurance rates, and legal claims.
Anthony Forest Products, a forest products firm, saved almost $1 million in workers’ compensation and other expenditures by investing $50,000 in safety and staff training from 2001 to 2006.
A secure workplace promotes employee morale and happiness. Being loved and cared for boosts engagement, productivity, and loyalty.
Organisations’ public image improves when they do frequent safety audits. This may boost brand reputation, talent retention, and consumer and partner trust.
Three common safety audit categories are:
Audits evaluate an organization’s safety compliance with laws, rules, and standards. These are usually done by external auditors with regulatory knowledge.
Compliance checks ensure your company is following the law and avoiding fines.
These audits assess your company’s safety policies, procedures, and initiatives. They usually involve:
Program audits uncover ways to enhance safety programs to protect workers and avoid accidents.
Your safety management system’s efficacy is assessed by these audits. They examine how your safety program’s components work together to ensure workplace safety.
Expert auditors who understand safety management systems do this audit. The correct safety audit depends on the organization’s needs and risk profile. However, all three types of audits may help organisations improve workplace safety and compliance.
Organisations must prioritise workplace safety. Auditing workplace safety regularly helps detect dangers, check compliance, and take remedial action.
Step-by-step instructions for a successful workplace safety audit:
Workplace safety audits require the proper audit team.
Diversity is key to an effective audit team. Include your most knowledgeable Osha-savvy safety officials. Include operations, maintenance, engineering, etc. representatives. Their local knowledge can be useful.
Consider external auditors every several years. An outsider’s perspective reveals internal team blind spots. More individuals imply more knowledge and observations.
An audit team may comprise the safety coordinator, maintenance supervisor, warehouse manager, machine operators, and a third-party safety expert.
A checklist and review of the company’s safety practices may help the audit team. The checklist may uncover areas that require further attention. In addition, the organisation must compare the location’s existing activities to its future aspirations.
Perform a Preliminary Risk Assessment
Perform a risk assessment before the audit to detect urgent issues. Risk assessments examine incident reports, near-miss occurrences, and audit results.
Examples of considerations:
Safety audit preparation may involve assigning tasks to team members. Two team members can gather samples while others interview.
The audit team finds hazards. This focusses their efforts on the most relevant regions and improves audit efficiency.
In one year, OSHA examined almost 39,000 organisations. Over 17,000 inspections were “programmed”—random safety assessments.
Assess workplace conditions with thorough on-site inspections. Check the whole facility for hazards, equipment, machinery, storage, ventilation, and emergency exits.
Consider these elements while assessing the workplace:
illumination: Check the room illumination to verify if individuals can see and operate machines safely. Check warehouse high-intensity discharge lighting’ efficacy. Check fixtures for enough lightbulbs.
Equipment placement: Make sure the firm has properly kept and accessible equipment. Check ladder storage to make sure it doesn’t block paths.
Workplace Ergonomics: Benefits and Improvements
Signage: Look for signs warning about dangerous materials and mechanical use. Even with extensive training, putting signs in the workplace improves safety. This also demonstrates the company’s safety focus.
Document defects, noncompliance, and safety concerns. Employees can provide valuable insights and direct knowledge about workplace safety measures during inspections.
Most audits fail due to poor safety documentation! Update all equipment and material permissions, licenses, and registrations first.
Check logs and records for inspections, safety training, incident investigations, and more. Check if supervisors record safety and behaviour observations regularly. Check a sample of these inputs for correctness.
Look for missing, obsolete, or incomplete records that might put you in non-compliance. Well-maintained paperwork shows your safety commitment.
All-level employee interviews for a successful safety audit
Human interaction yields invaluable information that observers cannot. Talk to staff about safety and give anonymous questionnaires. Assess their knowledge, comfort, and viewpoints, raising issues. Ask whether they’ve met any risks and what their plan is.
Questions include:
Their answers will disclose your workplace’s safety culture.
Now it’s time to analyse inspection, interview, document, and walkthrough data. Methodically evaluate the outcomes against your scope and rules.
Prioritise the most urgent dangers. Avoid ignoring tiny difficulties, which might lead to major risks. Provide realistic suggestions for process redesign, equipment upgrades, and training.
Document everything in a brief safety program baseline report. Be honest with department heads and leaders about critical results. Their advice is essential for prevention.
Safety audits only function if they improve and avoid workplace hazards. Assign remedial measures to appropriate teams and enforce deadlines.
Be careful not to assign and forget! As safety leader, you must regularly monitor actions to guarantee compliance. Brief on each measure’s impact and relevance. Celebrate wins to motivate.
Discover ways to showcase audit results through displays, reports, and more. Use technology to track activities, automate notifications, and monitor safety metrics in real time.
Remote and hybrid work patterns require a new approach to employee safety and well-being. Traditional safety assessments for physical workstations typically fail to meet these non-traditional locations’ specific issues and considerations.
Remote and hybrid workplace safety audit strategies:
Remote workers prevent auditors from inspecting workstations. Instead, check home office ergonomics using photos, videos, or virtual tours. Employees can also use safety audit checklists to self-assess their posture, computer position, illumination, and other aspects.
To solve problems, experts propose adjustable seats, display mounts, keyboards, and more.
Evaluate psychosocial factors during remnote and hybrid workplace safety audits.
Remote employment raises psychological risks such
Lack of in-person engagement with coworkers can cause social isolation and loneliness, affecting mental health and motivation.
The blurring of work and personal life can cause overwork, stress, and burnout.
Remote communication and collaboration issues can cause misunderstandings, team disintegration, and productivity losses.
Lack of connection: Feeling disconnected from the company and coworkers can lower morale and engagement.
Psychosocial dangers may be addressed by:
Employee Surveys: Conduct private surveys to assess employee well-being and detect isolation, stress, task management, and work-life balance issues.
Integrating Mental Health Resources: Evaluate EAP and mental health resources. Promote two-way employee feedback.
To reduce isolation and create relationships, encourage regular communication, team-building (virtual and in-person where feasible), and social engagement.
To achieve a good work-life balance, encourage employees to take breaks, set limits, and use flexible work arrangements.
Study work hours, time off, and employee engagement.
Virtually evaluate fire exits, trip hazards, and more using photographs, films, or live streaming, just like ergonomics. Call workers for video interviews.
Inspect hybrid models onsite and virtually. Assure employees that these checks are for safety, not monitoring.
Assess staff safety involvement in training and inspections. Remote engagements may drop. Strategise to increase involvement using shorter e-trainings, online safety meetings, and anonymous feedback mechanisms.
The aforementioned inventive ideas allow organisations to maintain safety supervision despite new work model disruptions.
Even as operations change, employee health is paramount. After all, health is riches.
For maximum impact, firms may implement these safety audit best practices:
Maintain Safety via Audits
Instead of yearly safety evaluations, do more frequent inspections. Periodically rotate between corporate departments for complete coverage. For instance, quarterly audits for each key department minimise complacency and ensure safety measures are followed.
To comply with regulations, align audit methods with laws, rules, and industry norms. Adapt audit materials and checklists to OSHA and EPA criteria. Audits comply with corporate policy and external regulations.
Find the causes of safety issues instead than just recording them. Dig deeper to find systemic issues like inadequate training or equipment.
Repeated data breaches may force a review of cybersecurity policies and personnel training.
Classify audit results by severity and urgency to prioritise remedial actions. Address high-risk issues and continuously monitor action plans to finish on schedule. Automated reminders and audit management software simplify task management and responsibility.
Effective safety audits require competent and objective auditors.
Safety audits should be conducted by trained, unbiased specialists. The credibility and dependability of audit results improves their efficacy in improving organisational safety.
Always use audit-specific checklists, processes, and documentation templates. Free templates are available online, but they must be customised.
If the template includes chemical handling safety protocols but your corporate offices focus on administrative responsibilities, remove or change such portions. By customising these tools, you guarantee that your safety audits target your environment’s particular hazards and needs, making your workplace safer for everyone.
In conclusion, a comprehensive safety audit plays a vital role in maintaining a secure and healthy workplace. By identifying risks, ensuring compliance, and implementing corrective actions, companies can significantly reduce accidents, lower costs, and improve employee morale. Regular audits not only protect the organization from potential hazards but also demonstrate a commitment to worker safety, fostering trust and a positive workplace culture. Prevention is always better than cure—start your safety audits today to safeguard your most valuable asset: your employees.
Thank you! You've signed up for our newsletter.



















Overwhelmed by PPE options for food safety? Master your PPE selection for food workers safety with these practical tips.

Struggling to maintain clear vision in demanding environments? This guide is here to help. By the end, you’ll know exactly...

Electricians across Europe face unique challenges that require reliable safety glasses to ensure both protection and efficiency. Whether safeguarding against...

Overwhelmed by PPE options for food safety? Master your PPE selection for food workers safety with these practical tips.

Struggling to maintain clear vision in demanding environments? This guide is here to help. By the end, you’ll know exactly...

Electricians across Europe face unique challenges that require reliable safety glasses to ensure both protection and efficiency. Whether safeguarding against...
Get 10€ off on your first order!
Save 30% by buying directly from brands, and get an extra 10€ off orders over €100
Save 30% by buying directly form brands, and get an extra 10€ off orders over €100